IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) is the latest version of the Internet protocol, developed to replace IPv4 which is gradually being exhausted. In this article, Antidetect Browser Hidemium will help you learn what IPv6 is, clarify the difference between IPv6 and IPv4, and explore the outstanding benefits of IPv6 in the context of digital transformation and Internet of Things (IoT) development.
1. What is IPv6?
IPv6 stands for Internet Protocol version 6 – a new generation network protocol that allows devices to connect to the Internet through a unique IP address. While IPv4 only provides about 4.3 billion IP addresses, this number is no longer enough for global needs. IPv6 completely solves this problem thanks to its large address space, allowing billions of billions of devices to connect simultaneously with ease.

>>> Learn more: What is IP address? How to hide IP address
2. Outstanding benefits of IPv6
Below are the outstanding advantages of IPv6 over IPv4:
Virtually limitless address space: IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses, creating a huge number of IP addresses, meeting the need for continuous connectivity in the digital age.
End-to-end connectivity without NAT: IPv6 eliminates the NAT mechanism, allowing devices to communicate directly with each other, thereby optimizing network speed and performance.
Autoconfiguration: IPv6 supports stateless address autoconfiguration, reducing dependency on DHCP and making network administration simpler.
More efficient routing: Thanks to its hierarchical routing design, IPv6 helps reduce latency, improve data transmission efficiency, and reduce the load on the network system.
Superior Multicast Support: IPv6 supports simultaneous data transmission to multiple devices (Multicast), saving bandwidth and improving transmission efficiency.
Built-in security: IPv6 has built-in security protocols like IPsec, which encrypts data and authenticates users right at the network layer.
Optimized for mobile devices: IPv6 supports seamless roaming, helping mobile devices maintain stable connections when moving between different networks.

3. What are the components of an IPv6 address structure?
IPv6 is a new generation network protocol, providing a large address space and high security. Each IPv6 address is made up of three main parts, helping to identify and manage devices in the network effectively:
Site Prefix: This is a network or organization identifier, usually assigned by an Internet Service Provider (ISP). Site Prefix helps identify which network the address belongs to and is often shared by devices on the same network.
Subnet ID: Allows the main network system to be divided into many subnets, helping to organize and manage network infrastructure more flexibly and effectively.
Interface ID: Is a unique identifier for each device in the network, ensuring each device has a unique, non-duplicated address, thereby supporting accurate connection and routing.
>>> Learn more: IP location checker: automatically matches browser location settings with external IP address location settings
4. IPv6 address representation rules
At 128 bits long, IPv6 addresses can be quite complex to represent. However, there are some truncation rules that apply that simplify the reading and management of addresses while maintaining accuracy.
4.1. How to write IPv6 address
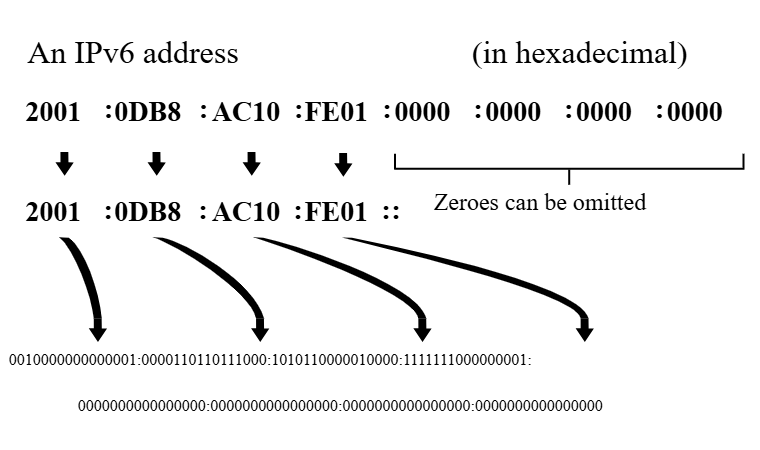
A full IPv6 address consists of 8 groups of 16 bits each, represented by 4 hexadecimal characters and separated by colons “:”. For example: FEDC:BA98:768A:0C98:FEBA:CB87:7678:1111.
To make it shorter and easier to read, the following two rules can be applied:
Dropping leading zeros: Leading zeros in each group can be dropped. For example, 0001 can be written as 1.
Use “::” to replace a group of all zeros: A series of consecutive groups of all zeros can be replaced with the symbol “::”. However, “::” should only be used once in each address to avoid confusion about the number of groups. For example, the address 1080:0000:0000:0070:0000:0989:CB45:345F can be shortened to 1080::70:0:989:CB45:345F.
4.2. Address Prefixes
Similar to IPv4 using CIDR, IPv6 also uses prefix format to represent network address range. The way to write it is as follows: IPv6-address/prefix-length.
IPv6-address: is a valid IPv6 address.
Prefix-length: the first number of bits in the address used as the network identifier prefix.
For example, the address 200F::AB00:0:0:0:0/56 can be shortened to 200F:0:0:AB00::/56.
Note: The “::” symbol is used only once in each address to ensure correct structure. Incorrect use, such as 200F::AB00/56, may result in missing necessary groups of numbers, leading to routing or addressing errors.
5. Comparison of IPv6 and IPv4
5.1 Similarities
IPv4 and IPv6 are two important Internet protocols that play a role in connecting devices and transmitting data over networks. Although IPv6 is the newer version, the two still have many notable similarities in how they work and what they are used for:
Same data routing function: Both IPv4 and IPv6 are responsible for transmitting and routing data on the Internet, helping information to be delivered to the correct destination device regardless of the network infrastructure.
Providing unique IP addresses: Every device connected to the Internet needs a unique IP address to be identified. Both protocols meet this requirement for devices such as computers, mobile phones, and IoT devices.
As a component of the TCP/IP protocol suite: IPv4 and IPv6 are both core protocols of the TCP/IP network protocol suite – the Internet communication standard since the 1980s. Although IPv4 was used very early and IPv6 was officially popularized in 2017, both still operate in parallel with other protocols such as TCP and UDP.
Connectionless data transmission: Both protocols break data into packets and transmit them over different paths on the Internet. The data restructuring is handled at the transport layer by protocols such as TCP or UDP.

5.2. Difference between IPv4 and IPv6: Comprehensive Comparison
IPv4 and IPv6 are two versions of the Internet protocol with different technical characteristics, directly affecting the performance, scalability and security of the network system. The table below helps you easily see the differences between IPv4 and IPv6 in many important aspects:
Criteria | IPv4 | IPv6 |
| Data Stream | Non-optimal format, sometimes affecting quality of service (QoS) | Clear format structure, more efficient QoS support |
| Packet fragmentation | Occurs at both Router and Host, easily causing data loss or delay | Only occurs at Host, minimizing risk and increasing transmission efficiency |
| Header Structure | Simple, no expansion support | Support extensions, flexibility and optimized packet processing |
| Checksum Header | Yes, it consumes resources and increases processing time | Remove checksum, improve network speed and performance |
| Broadcast | Use Broadcast to send to all devices in the network | Remove Broadcast, replace with Multicast to save bandwidth |
| Network group management | Use IGMP protocol to manage network members | Replaced with MLD, improved efficiency in subnetting |
| Identify Gateway | Using IGMP Router Discovery | Using MLD to detect default Gateway |
| Domain Name System (DNS) Mapping | Use A records to map host names to IPv4 addresses | Use AAAA record to map to IPv6 address |
In general, IPv6 brings many outstanding advantages such as larger address space, good QoS support, reduced latency and enhanced security. With the strong development of IoT and the need for continuous network expansion, switching to IPv6 is becoming an inevitable trend in the digital age.
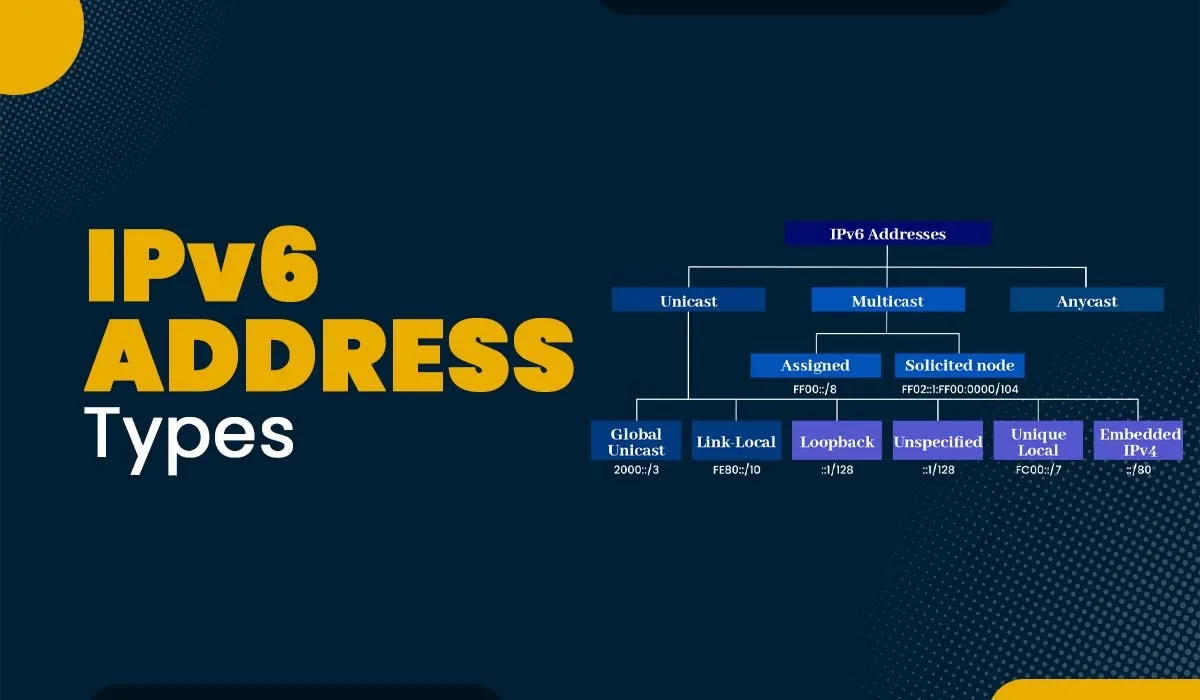
6. Common IPv6 address types and their functions
In the IPv6 protocol, there are three main types of addresses, each of which plays a specific role in the transmission and routing of data. Understanding the different types of IPv6 addresses not only helps in the efficient deployment of networks, but also ensures security and scalability in the modern digital environment.
6.1 Global Unicast Address
This is a type of address that is routable on the Internet, equivalent to a public IP address in IPv4. These addresses usually start with the prefix 2001: and are assigned by Internet resource management organizations or Internet service providers (ISPs). Global Unicast is usually configured through the SLAAC (Stateless Address Autoconfiguration) mechanism and allows devices to communicate globally in a flexible and secure manner.
6.2 Unique Local Address (ULA)
Unique Local Addresses are addresses that are used only within the internal network and are not accessible from the Internet. They start with the prefix fd00::/8 and are often used to ensure privacy and security in business or home networks. ULAs are usually manually configured and are important in internal applications where isolation from the outside network is required.
6.3 Link-Local Address
Link-Local addresses are valid only within the same network segment and cannot be routed out. They start with the prefix fe80:: and are automatically generated when a device connects to a network, even if there is no DHCP server. They are equivalent to the IPv4 address range 169.254.0.0/16 and are required on every IPv6 network interface to ensure internal communication.
>>> Learn more:How to find Facebook IP address using mobile phone
7. Instructions for Checking IPv6 Connection on Your Device
To ensure that your device is properly configured and capable of using IPv6 addresses, you should perform a few simple checks. This will not only confirm support from your Internet Service Provider (ISP), but also ensure a stable connection to modern platforms that use the IPv6 protocol.
7.1. How to Check If Your ISP Supports IPv6
You can determine whether your carrier supports IPv6 by using the online tool at test-ipv6.com.
This tool helps you know whether your current connection is using IPv4 or IPv6, showing you the details of the IP address and the name of your Internet service provider. At the same time, it also checks the ability to access IPv6-enabled websites, thereby helping you evaluate whether your network configuration is suitable for IPv6 or not.
7.2. Check if Your Device is IPv6 Ready
There are two simple ways to check if your computer supports IPv6:
Method 1:Use tools from Google
Visit ipv6test.google.com to test your computer's IPv6 connectivity. This tool will provide a quick readout of whether your device can access the Internet via IPv6 and detect problems (if any) with websites that use IPv6.
Method 2:Use the advanced IPv6 test page
You can visit ipv6-test.com to get a more detailed look at your current connection. This site will analyze the protocol you are using (IPv4 or IPv6), your IP address, your Internet service provider, and your browser's IPv6 preference. If your browser is not yet prioritizing IPv6, you may need to restart your browser for the changes to take effect.
8. Frequently asked questions about IPv6 addresses
If you are learning about IPv6, below are common questions and detailed answers to help you better understand the transition from IPv4, how to protect IP addresses, and the benefits of using IPv6 in the digital age.
8.1. When is the right time to switch to IPv6 addresses?
Moving to IPv6 addresses should be considered in the following situations:
IPv4 address limitation: When you encounter IPv4 address exhaustion or need to expand your network with more devices.
Expanded connectivity requirements: IPv6 increases connectivity between devices, especially in large systems or enterprise environments.
Enhanced network security: IPv6 integrates stronger security features, supports new technologies such as IoT, and helps protect systems against increasingly sophisticated threats.
8.2. How to protect personal IP address?
To keep your IP address and personal data safe, you should take the following measures:
Keep your devices up to date: Make sure your router, computer, and software are all up to date with the latest security patches.
Use VPN: A solution to hide your real IP address, encrypt your connection and increase your privacy while surfing the web.
Manage app access: Set reasonable privacy settings for apps on your phone and tablet.
Enable firewall: Use firewalls in conjunction with security software to prevent unauthorized access to your network.
8.3. How many bits does an IPv6 address have?
IPv6 addresses are designed with 128 bits – many times larger than IPv4 addresses which only have 32 bits. This creates a virtually limitless address space, serving the needs of connecting billions of devices in the Internet of Things (IoT) era.
8.4. Should we switch to IPv6?
If you are limited by IPv4 or want to optimize your network for the future, moving to IPv6 is a smart choice. Some of the notable benefits:
Huge address space: Gives your network the flexibility to scale without limits.
Built-in security: IPv6 supports better authentication and encryption, helping to protect data effectively.
Support for new devices and technologies: Especially suitable for the trend of connecting things (IoT) and modern platforms.
This article has answered frequently asked questions about IPv6 addresses and guided you to better understand the reasons for switching from IPv4. In the era of comprehensive connectivity, IPv6 plays a key role in securing, expanding and optimizing network systems. Hidemium is always ready to accompany and support you in the journey of upgrading technology infrastructure, ensuring efficiency and safety for the digital future.
Related Blogs
1. Open the Hidemium app, and select New browser Profile. 2. Click on Proxy settings. 3. From the dropdown menu select SOCKS5 proxy. Open the IP2World app, follow the arrow 4. Select the proxy type, then paste the copied proxy IP and port into it, and finally click Check Proxy Hidemium
In today’s digital age, using sample Prompt Scripts to automate browser tasks is becoming more and more popular, especially when combined with the Hidemium antidetect browser. With the powerful support of AI models like ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini, users can easily perform tasks such as form filling, page scrolling, or content analysis – all without any coding knowledge.This article will[…]
Let's start with a question: what device are you using to read this content? A reasonable guess would be a smartphone or a laptop, or perhaps even a used desktop. Over the past decade, smartphones have gradually outpaced desktop computers, making it harder for other devices to compete in terms of internet access. The only remaining competitor is the laptop, but in many cases, it has also taken a[…]
In today's challenging Digital Marketing environment, protecting accounts and safeguarding user information has become a top priority. Antidetect Browser plays a key role in protecting identities and optimizing online marketing strategies. With its ability to mask information and block tracking activities, this tool not only supports the effective management of multiple advertising accounts but[…]
Các Bước Tạo Script Automation Cho Người Mới Bắt Đầu. Một tính năng mang tính đột phá và hiện đại trong phần mềm Hidemium mà bạn không thể bỏ qua đó chính là Automation. Tính năng này cho phép người dùng có thể tạo ra những kịch bản (script) cho những quy trình phục […]
Did you know? More than 25% of professional eBay sellers are using multiple accounts to increase revenue, spread risk, and avoid permanent bans. However, managing multiple eBay accounts without getting caught is a major challenge—unless you have the right tools.If you are really interested in multi-account eBay, selling anonymously or implementing dropshipping at scale, you've probably[…]



.png)

