In a network system, MAC address and IP address Both serve to identify devices, but they perform completely different functions. Understanding the difference between these two types of addresses not only helps you manage your network better, but is also key to ensuringinformation security – especially for those working in the field Cyber Security or digital marketing.
Let's go together Hidemium Read on to understand each address type and how they work in your network.
1. What is a MAC address?
MAC Address (Media Access Control) can be understood as the “permanent identifier” of a network device. Whether you are using laptop, smartphone good printer, each device has a unique MAC address – and this address doesn't change, no matter what Wi-Fi network you connect to.
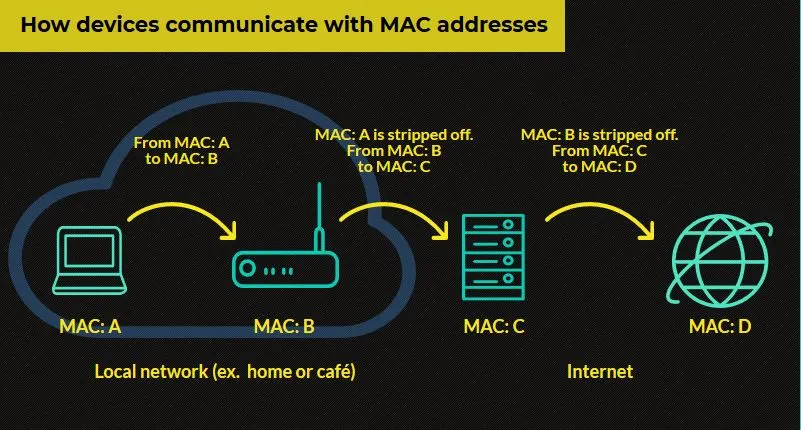
MAC addresses help devices in the same local area network (LAN) can recognize and communicate with each other.
1.1 Structure and format
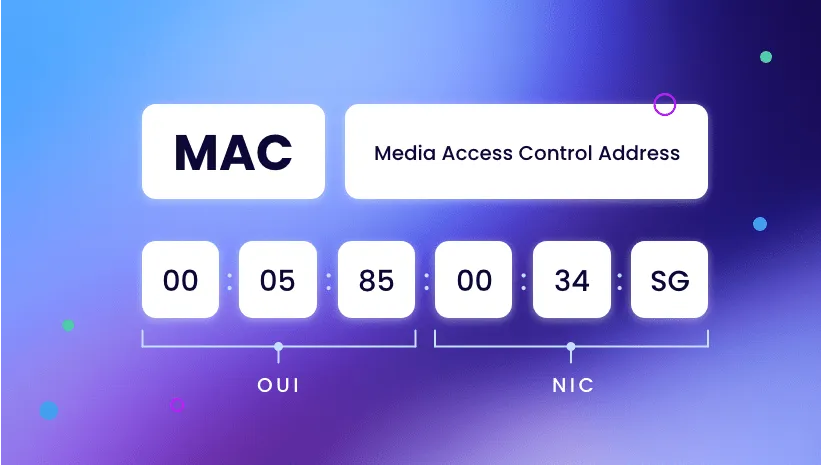
MAC address is a sequence of numbers 48 bit, usually represented as 12 hexadecimal characters. Divide into 6 pairs, for example:00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E. The structure consists of two parts:
Manufacturer Identifier (OUI): The first 6 characters (24 bits) represent the network device manufacturer.
Device code: The last 6 characters (remaining 24 bits) are unique for each device, ensuring no duplicates.
1.2 Functions and practical applications
When devices are connected to the same LAN, MAC addressused to pinpoint the exact destination of data. For example, when you print a document from your laptop over Wi-Fi, the system uses the MAC address to ensure the file is sent to the correct printer – avoiding being mistakenly sent to a nearby device.
In addition, network devices such as switch also relies on MAC addresses to route data more accurately and optimally.
1.3 Hardware-specific fixed features
Unlike an IP address – which can change every time a device connects to a new network – MAC address is built into the hardware. This makes it an identifier stable and reliablein managing devices on the network. Unless you actively change it through software, the MAC address will always remain the same from the time the device is manufactured.
Understanding the difference between MAC address and IP address Not only does it help you use your network devices more efficiently, it's also the first step in your journey to protecting your privacy and personal security.
>>> Learn more: What is MAC Address? Check, Types and Practical Uses
2. What is an IP address?
Think of an IP (Internet Protocol) address as the “home address” of a device when it connects to the Internet. It is a unique series of numbers that uniquely identifies each device, allowing them to communicate with each other over the network efficiently and accurately.
IP addresses play an important role in routing data. When you visit a website or send information, your IP address helps ensure that the data gets to the right place – just like the post office needs to know the recipient's address to deliver the letter.
2.1 IP address structure and format
Currently, there are two popular versions of IP addresses IPv4 and IPv6:
IPv4 is the most widely used form of address. It consists of four groups of numbers, separated by periods – for example:196.166.1.1. Each group has a value from 0 to 255. This type of address is enough to provide millions of devices with independent network access.
IPv6 was born to meet the need to expand the number of Internet-connected devices IPv6 address has a structure of 8 groups of characters separated by colons
For example: 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334. Thanks to this design, IPv6 provides a virtually unlimited number of IP addresses.
2.2 Function and operating mechanism
Every device connected to the network is assigned a unique IP address, which identifies it and routes data. When you open a website, your device sends a request to the server using its IP address. The server then responds by sending data back to your device's correct IP address, allowing the content to be displayed in your browser.
2.3 Distinguish between dynamic and static IP addresses
Dynamic IP Address is an address that is automatically assigned by a router or DHCP server. This type of address can change with each connection session and is commonly used in home or small office networks.
Static IP address is a fixed address, set manually and does not change over time. It is often applied to devices that require high stability such as servers, surveillance cameras or network printers.
A real-world example of these two types of IP addresses are the forms proxy:
Mobile Proxy (based on 3G/4G network) uses dynamic IP, constantly changing - suitable for activities that require high anonymity or avoid being detected by the system.
Meanwhile, residential proxy, static proxy, dedicated proxy or ISP proxy provides a fixed IP address, making the connection more stable and ideal for maintain accounts, manage systems or do long term online business.

>>> Learn more: How to hide your IP address
3. What is the difference between MAC address and IP address?
MAC addresses and IP addresses both play an important role in identifying devices in a computer network, however, each has its own distinct function, structure, and usage.
Criteria | MAC Address | IP Address |
| Full name | Media Access Control - Media Access Control Address | Internet Protocol Address - Internet Protocol Address |
| Structure | Consists of 48 bits (6 bytes), represented in hexadecimal form | Consists of 32 bits (IPv4) or 128 bits (IPv6), represented in decimal or hex form |
| Function | Identify hardware devices in the network | Locate the device in the network system |
| Belong to the floor | Data Link Layer – hardware related | Network Layer – related to software |
| Distribution method | Fixedly assigned by the network card (NIC) manufacturer | Assigned by ISP (internet provider) or configured by user |
| Ability to change | Fixed, almost unchangeable | May vary depending on location or network used. |
| Protocol used | Works with ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) | Using RARP (Reverse ARP) protocol |
| Security | Less susceptible to detection by unauthorized users | Vulnerable to third-party scanning and tracking |
| Related equipment | Switch used for routing by MAC address | Router used for routing by IP address |
| Display format | 6 pairs of hexadecimal characters, for example: 00:FF:FF:AB:BB:AA | IPv4: 192.168.1.1 or IPv6: FFFF:F200:3204:0B00 |
| Classify | No classification | There is a hierarchical classification (A, B, C, D, E in IPv4) |
| Shareability | Unique to each device – cannot be shared | Can be shared between multiple devices in a network |
4. Tracking Devices by MAC and IP Address: How It Works and How to Protect Privacy
Tracking devices using MAC and IP addresses is a common method used in both local and online environments. Understanding how these two types of addresses work will help you gain more control over your personal information and privacy.
4.1. Tracking via MAC address
A Media Access Control (MAC) address is a unique identifier assigned to the networking hardware on your device, such as a Wi-Fi card. When you connect to a local network — such as your home, coffee shop, or office Wi-Fi — the MAC address is used to identify your device and record activities on that network.
In fact, many businesses that offer free Wi-Fi often use MAC addresses to track user behavior, such as how long they stay in each area of the store or how often they return. This information helps improve the quality of service, but also raises concerns about personal privacy.
To overcome this, most modern devices today support the feature of generating random MAC addresses when searching for Wi-Fi networks, helping to reduce the possibility of being tracked.
4.2. Tracking via IP address
Unlike a MAC address, which is only used on a local network, an IP (Internet Protocol) address is used to identify your device when accessing the Internet. Every time you open a website or use an online service, the IP address helps route data between your device and the server.
Using your IP address, websites can determine your approximate location — such as the city or region you're visiting — and track your browsing behavior to personalize the content or ads they display. IP addresses are also logged to analyze user interactions and improve system performance.
To protect privacy, users can use VPNs or proxies to hide or change their real IP addresses. These tools help conceal their real location and reduce the possibility of being tracked when accessing the Internet.
>>> Learn more:IP Checker: automatically matches browser location settings with external IP address location settings
5. Why should I change my MAC and IP address?
Changing your MAC or IP address is often done to protect your privacy, improve network access, or troubleshoot technical issues. Here are some common reasons why individuals and organizations choose to change these two types of addresses:
5.1. Protecting privacy and enhancing online anonymity
One of the most important reasons to change your MAC or IP address is to protect your privacy and remain anonymous when accessing the internet. Your IP address can reveal your location and online habits, making you vulnerable to tracking by websites and digital services. Therefore, changing your IP address periodically or using a VPN will help you limit the collection of your personal data.
Additionally, each device has a unique MAC address, which can be used to track your activity across multiple networks. Especially when connecting to public or semi-public networks, periodically changing your MAC address can help increase your privacy and reduce surveillance.
5.2. Bypass network access restrictions and blocks
In some cases, network administrators may use IP or MAC addresses to restrict access to websites, services, or internal networks. If your IP address is blocked, changing to a new IP address will restore your normal access.
Similarly, some networks also apply filters based on MAC addresses. In this case, changing your MAC address can help you avoid the blocks. While this is less common than changing your IP, it is still an effective solution in certain situations.
5.3. Troubleshooting network conflicts
IP address conflicts often occur when multiple devices on the same local network are assigned the same IP, causing connection disruption and affecting system performance. In this case, reassigning IP addresses to each device will help stabilize the network connection.
Similarly, if two devices share the same MAC address on the same network, there is a risk of errors during data transmission. Changing the MAC address for one of the two devices will help resolve the conflict and ensure smooth network operation.
5.4. Avoid becoming the target of cyber attacks
Cybercriminals often use MAC or IP addresses to identify and target specific devices. Changing these identifiers makes it harder for bad guys to track or attack you. This is especially important if you suspect your device is being tracked or if you frequently experience security issues.
5.5. Network testing and troubleshooting support
For network administrators and IT professionals, changing MAC and IP addresses is an important step in the testing, assessment, and troubleshooting process. This helps simulate various network scenarios, test system configurations, and accurately diagnose errors, thereby improving overall operational efficiency.
5.6. Enhance device security
In many cases, changing your MAC address is an effective way to prevent unfamiliar or unauthorized devices from accessing your network. If you suspect that your MAC address is being spoofed or has been leaked, updating it to a new address will help protect your device from potential attacks and increase the security of your entire system.
>>> Learn more: How to connect 2 computers via IP address simply and effectively
6. Does a VPN hide your MAC address? Why can some websites and social networks still "see" you even when using a VPN?
While VPNs are an effective tool for protecting your identity and hiding your IP address, there are still many websites and social networks that can track and identify you. This is because there are many modern techniques that can bypass VPN security, including:
Browser Fingerprinting:
Some websites use browser fingerprinting to collect detailed information about your device, browser settings, and usage habits. These characteristics can create a “unique fingerprint” that identifies you, even if you’re connected via a VPN.
Device Fingerprinting:
Similar to browsers, platforms also employ techniques to collect information about your device's hardware, software, and configuration. This data is enough to bypass VPN protection and indirectly identify users.
Cookies and tracking scripts:
Cookies and tracking scripts may remain in your browser, saving you from previous visits. Even if you have a VPN enabled, these tools can still track your activity across multiple browsing sessions. Use a cookie manager to control and delete unnecessary data.
Login information:
When you log into a personal account like social media or email while using a VPN, the system can still link your online activity to your real identity. This is one of the weaknesses that VPNs cannot completely hide.
IP Leak:
In some cases, VPNs can have flaws like DNS or WebRTC leaks that expose your real IP address. When this happens, websites can detect and track you just as if you weren't using a VPN.
7. Common methods to change MAC address and IP address
7.1 On Windows 10 and Windows 11
How to change IP address:
You can easily change your IP address on Windows by disconnecting and reconnecting to the network to get a new IP from the router, or setting it up manually through the control panel. Access Settings > Network & Internet > Status > Change adapter options, double-click the connection in use, selectProperties, then select Internet Protocol version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and enter the new IP address.
How to change MAC address:
Open Device Manager, go to the item Network adapter, right click on the adapter you are using and select Properties. In tab Advanced, find item Network address (or Local admin address) and enter the desired MAC address. Note: not all adapters support this feature.
7.2 On macOS
How to change IP address:
On macOS, you can go to System Preferences > Network, select current connection, press Advanced, switch to tab TCP/IP and change IP by entering manually or select DHCP for the system to automatically allocate IP.
How to change MAC address:
Open Terminal and use the command:
Replace en0 by network interface name and xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx with the MAC address you want to use. Note: this change is only temporary and will automatically return to the original address after the machine restarts.
7.3 On iOS
How to change IP address:
Enter Settings > Wi-Fi, select the network you are connected to, then turn it off and on again Auto connect to let the device get a new IP. If you want to set a static IP address, select IP Configuration > Manual and enter the desired IP.
How to change MAC address:
iOS feature support Private address, allows the device to automatically use a random MAC address when connecting to Wi-Fi. To enable, go to Settings > Wi-Fi, select the network you are connected to, tap the "i" icon and turn it on Private address.
7.4 On Android
How to change IP address:
Access Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi, select the Wi-Fi network you are using, then go to the sectionAdvanced, transfer IP Settings from DHCP sang Static to enter IP address manually.
How to change MAC address:
Changing the MAC address on Android usually requires root access. For rooted devices, you can use a third-party app to change the MAC address. For non-rooted devices, you can still use a random MAC address by enabling the MAC address randomization in: Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi > Advanced > MAC address type.
>>> Learn more: How to change IP address on iPhone and Android phones quickly
8. Modern method to change MAC and IP safely: Antidetect Browser
Antidetect Browser is a state-of-the-art security solution designed to completely prevent personal information from leaking while browsing the internet. With the ability to create multiple separate browser profiles, each with a completely new device fingerprint — including MAC address, IP address, and over 50 other system parameters — antidetect allows you to browse the web as a completely different user.
Although most anti-detect browsers are developed for commercial purposes, especially in the digital marketing field, many tools still offer trial packages or free versions for personal use. Some browsers also integrate an effective IP proxy management feature, helping users maintain a stable state of anonymity.
Instead of manually changing your MAC or IP address, you can use an anti-detection browser like Hidemium to automate this process. With its comprehensive camouflage capabilities, Hidemium is currently the top choice of many digital marketers, especially when working with social media.
8.1 How does Hidemium work?
Hidemium is one of the leading tools for digital identity protection today. Unlike solutions that simply mask or encrypt your real MAC and IP addresses, Hidemium provides a new, transparent, and valid device identity – the equivalent of you accessing from a completely different device.
Thanks to advanced device fingerprint emulation technology, Hidemium almost completely eliminates the possibility of being tracked, even on platforms with strict surveillance systems such as cryptocurrency exchanges or major social networks.
Unlike VPNs, which encrypt data but keep the original parameters intact, Hidemium creates a new browsing environment with clean MAC, IP and fingerprint addresses taken from the proxy system. This allows you to operate online in a state of absolute anonymity.
8.2 How does Hidemium support business marketing?
In an increasingly competitive digital marketing environment, maintaining anonymity and security while managing multiple accounts is key. Hidemium allows businesses to operate flexibly across social media platforms without worrying about being blocked or losing access.
Specifically, if you run an advertising team with multiple Facebook accounts, using Hidemium will help you create each account on a separate browser profile, avoiding device linking and mass locking.
With a friendly and easy-to-use interface, Hidemium is highly rated on G2 and many professional platforms. This is an indispensable tool for marketers who want to optimize operations, protect their identity from risks such as MAC theft, account loss or device fingerprint-based attacks.
9. Conclusion
A MAC address is a 48-bit physical identifier assigned to each device on a local network. It is what uniquely identifies hardware when it connects to a network. In contrast, an IP address acts as a temporary identifier when a device accesses the internet. The IP can be static or dynamic depending on your network service provider or the type of connection you are using.
Changing your MAC or IP address not only helps users bypass access barriers, but also increases privacy and security, reducing the risk of being tracked. Although VPN is a popular solution to hide IP, in today's technological age, this is no longer enough. Many modern websites use this technique device fingerprinting to collect browser and hardware information to more accurately identify users.
So, to effectively anonymize, specialized tools like Hidemium – anti-detection browser is the ultimate choice. Hidemium not only replaces IP and MAC addresses but also creates a completely new device fingerprint, helping you maintain complete privacy. In particular, Hidemium now offers free package for personal use – the perfect solution for those looking for anonymity and security when accessing the internet. Try it today!
Related Blogs
The world of e-commerce and dropshipping is growing rapidly, with more and more businesses looking to take advantage of the opportunities presented by online sales. However, with this growth comes an increase in online fraud, which can lead to account locks, chargebacks, and other financial losses. To prevent these issues, many businesses are turning to […]
In the digital era, making money online (MMO) has become a popular trend, offering flexible and accessible opportunities for everyone. Whether you want to earn extra income or build a long-term business, there are always suitable options available. However, for beginners, the abundance of information can be overwhelming. Don’t worry! This article will guide you through 22 practical ways to make[…]
What Are AI Agents for HR and How to Integrate Them Into an Existing BusinessAnyone who’s worked in HR knows the routine: piles of resumes, endless follow-ups, and calendars packed with interviews that get delayed, cancelled, and end up ruining your schedule daily. The new wave of AI agents for HR and recruiting is quietly changing that.These systems don’t hire or fire on their own. They handle[…]
MarsProxies and Hidemium: Integration Guide Managing multiple accounts from a single device has long been essential, especially for those handling numerous advertising, e-commerce, or social media accounts. An effective anti-detect browser simplifies this by isolating each account’s browser profile, cookies, and data, allowing safe management of multiple accounts without letting target websites[…]
BitBrowser 2025 – A Simple and Powerful Anti-Detect Browser for Multi-Account Management Managing multiple online accounts across platforms has become a daily necessity for marketers, e-commerce sellers, crypto users, and digital professionals. However, the risks of account linkage, bans, and privacy leaks are more real than ever. That’s where BitBrowser comes in—a robust anti-detect browser[…]
In the digital age, using two computers in parallel to serve work is becoming more and more popular. To optimize performance and share data easily, connecting 2 computers via IP address is a useful solution, especially when both devices are on the same local network. Here are detailed instructions on how to do it.Antidetect Browser Hidemium:1. How to connect 2 computers via internal IP[…]




.png)
